Improved Precision of Mouse Retina Segmentation from Optical Coherence Tomography
Project Details
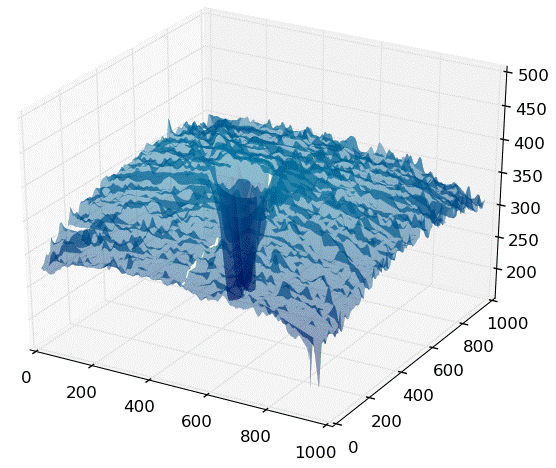
Background: The goal of this project was to improve the precision of a 3D segmentation algorithm that was challenged by noise and outliers. 2D frames were being processed independently, contributing to some of the noise. Analysis revealed by 3D plots showed the presence of background noise from the imaging device, structured noise caused an oscillation due to breathing, and outlying points near the edge of the scan and around internal structures. A solution to handle these complications also needed to run in a reasonable time.
Solution: A sequence of steps was developed that included aligning adjacent slices, robustly removing outliers, interpolating missing points, smoothing the segmentation, and cropping the bounds of the retina. A functional prototype was produced, and the segmentation accuracy was measured before and after implementation to verify the improvements.
Additional Applications: The techniques used in this project can applied as post-processing whenever an initial algorithm produces an excessively noisy output. Understanding the modalities of noise enables the best selection of noise reduction and clean up techniques.